- java.lang.Object
-
- reactor.core.publisher.Flux<OUT>
-
- reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor<T,T>
-
- reactor.core.publisher.ReplayProcessor<T>
-
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- Processor<T,T>, Publisher<T>, Subscriber<T>, CoreSubscriber<T>, Disposable, Fuseable, Scannable
public final class ReplayProcessor<T> extends FluxProcessor<T,T> implements Fuseable
Replays all or the last N items to Subscribers.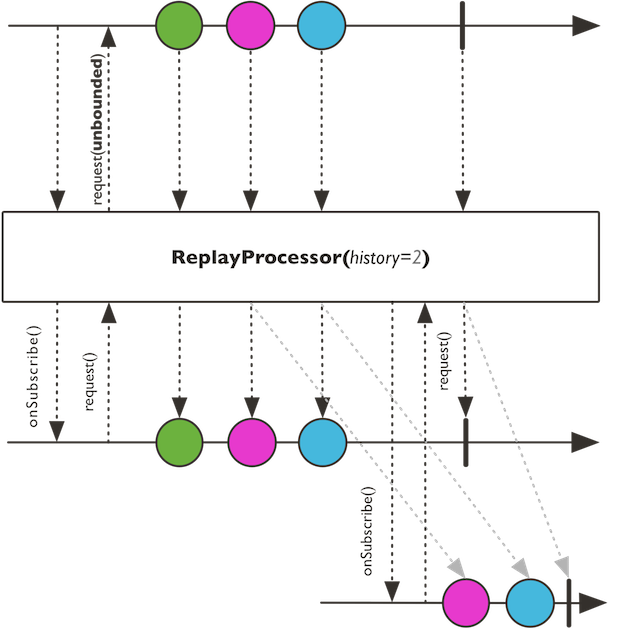
-
-
Nested Class Summary
-
Nested classes/interfaces inherited from interface reactor.core.Fuseable
Fuseable.ConditionalSubscriber<T>, Fuseable.QueueSubscription<T>, Fuseable.ScalarCallable<T>, Fuseable.SynchronousSubscription<T>
-
Nested classes/interfaces inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
Scannable.Attr<T>
-
Nested classes/interfaces inherited from interface reactor.core.Disposable
Disposable.Composite, Disposable.Swap
-
-
Field Summary
-
Fields inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
OPERATOR_NAME_UNRELATED_WORDS_PATTERN
-
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>cacheLast()Create aReplayProcessorthat caches the last element it has pushed, replaying it to late subscribers.static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>cacheLastOrDefault(T value)Create aReplayProcessorthat caches the last element it has pushed, replaying it to late subscribers.static <E> ReplayProcessor<E>create()Create a newReplayProcessorthat replays an unbounded number of elements, using a default internalQueue.static <E> ReplayProcessor<E>create(int historySize)Create a newReplayProcessorthat replays up tohistorySizeelements.static <E> ReplayProcessor<E>create(int historySize, boolean unbounded)Create a newReplayProcessorthat either replay all the elements or a limited amount of elements depending on theunboundedparameter.static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>createSizeAndTimeout(int size, Duration maxAge)Creates a time- and size-bounded replay processor.static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>createSizeAndTimeout(int size, Duration maxAge, Scheduler scheduler)Creates a time- and size-bounded replay processor.static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>createTimeout(Duration maxAge)Creates a time-bounded replay processor.static <T> ReplayProcessor<T>createTimeout(Duration maxAge, Scheduler scheduler)Creates a time-bounded replay processor.ContextcurrentContext()Request aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.longdownstreamCount()Return the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.ThrowablegetError()Current error if any, default to nullintgetPrefetch()The prefetch configuration of theFluxStream<? extends Scannable>inners()Return aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)booleanisTerminated()Has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?voidonComplete()voidonError(Throwable t)voidonNext(T t)voidonSubscribe(Subscription s)Implementors should initialize any state used bySubscriber.onNext(Object)before callingSubscription.request(long).ObjectscanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)This method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place.voidsubscribe(CoreSubscriber<? super T> actual)An internalPublisher.subscribe(Subscriber)that will bypassHooks.onLastOperator(Function)pointcut.-
Methods inherited from class reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor
dispose, getBufferSize, hasCompleted, hasDownstreams, hasError, isSerialized, serialize, serializeAlways, sink, sink, switchOnNext, wrap
-
Methods inherited from class reactor.core.publisher.Flux
all, any, as, blockFirst, blockFirst, blockLast, blockLast, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferUntil, bufferUntil, bufferWhen, bufferWhen, bufferWhile, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cancelOn, cast, checkpoint, checkpoint, checkpoint, collect, collect, collectList, collectMap, collectMap, collectMap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectSortedList, collectSortedList, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, compose, concat, concat, concat, concat, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatMap, concatMap, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapIterable, concatMapIterable, concatWith, concatWithValues, count, create, create, defaultIfEmpty, defer, delayElements, delayElements, delaySequence, delaySequence, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delayUntil, dematerialize, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, doAfterTerminate, doFinally, doFirst, doOnCancel, doOnComplete, doOnDiscard, doOnEach, doOnError, doOnError, doOnError, doOnNext, doOnRequest, doOnSubscribe, doOnTerminate, elapsed, elapsed, elementAt, elementAt, empty, error, error, error, expand, expand, expandDeep, expandDeep, filter, filterWhen, filterWhen, first, first, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMapDelayError, flatMapIterable, flatMapIterable, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequentialDelayError, from, fromArray, fromIterable, fromStream, fromStream, generate, generate, generate, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupJoin, handle, hasElement, hasElements, hide, ignoreElements, index, index, interval, interval, interval, interval, join, just, just, last, last, limitRate, limitRate, limitRequest, log, log, log, log, log, log, map, materialize, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, mergeDelayError, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrderedWith, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeWith, metrics, name, never, next, ofType, onAssembly, onAssembly, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureError, onBackpressureLatest, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorStop, onLastAssembly, onTerminateDetach, or, parallel, parallel, parallel, publish, publish, publish, publish, publishNext, publishOn, publishOn, publishOn, push, push, range, reduce, reduce, reduceWith, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeatWhen, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, retry, retry, retry, retry, retryBackoff, retryBackoff, retryBackoff, retryBackoff, retryBackoff, retryWhen, sample, sample, sampleFirst, sampleFirst, sampleTimeout, sampleTimeout, scan, scan, scanWith, share, single, single, singleOrEmpty, skip, skip, skip, skipLast, skipUntil, skipUntilOther, skipWhile, sort, sort, startWith, startWith, startWith, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribeOn, subscribeOn, subscriberContext, subscriberContext, subscribeWith, switchIfEmpty, switchMap, switchMap, switchOnFirst, switchOnNext, switchOnNext, tag, take, take, take, takeLast, takeUntil, takeUntilOther, takeWhile, then, then, thenEmpty, thenMany, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timestamp, timestamp, toIterable, toIterable, toIterable, toStream, toStream, toString, transform, using, using, usingWhen, usingWhen, usingWhen, window, window, window, window, window, window, window, windowTimeout, windowTimeout, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowWhen, windowWhile, windowWhile, withLatestFrom, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWithIterable, zipWithIterable
-
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait
-
Methods inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
actuals, from, isScanAvailable, name, parents, scan, scanOrDefault, stepName, steps, tags
-
Methods inherited from interface reactor.core.Disposable
isDisposed
-
-
-
-
Method Detail
-
cacheLast
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> cacheLast()
Create aReplayProcessorthat caches the last element it has pushed, replaying it to late subscribers. This is a buffer-based ReplayProcessor with a history size of 1.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the pushed elements- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays its last pushed element to each newSubscriber
-
cacheLastOrDefault
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> cacheLastOrDefault(@Nullable T value)
Create aReplayProcessorthat caches the last element it has pushed, replaying it to late subscribers. If aSubscribercomes in before any value has been pushed, then thedefaultValueis emitted instead. This is a buffer-based ReplayProcessor with a history size of 1.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the pushed elements- Parameters:
value- a default value to start the sequence with in case nothing has been cached yet.- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays its last pushed element to each newSubscriber, or a default one if nothing was pushed yet
-
create
public static <E> ReplayProcessor<E> create()
Create a newReplayProcessorthat replays an unbounded number of elements, using a default internalQueue.- Type Parameters:
E- the type of the pushed elements- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays the whole history to each newSubscriber.
-
create
public static <E> ReplayProcessor<E> create(int historySize)
Create a newReplayProcessorthat replays up tohistorySizeelements.- Type Parameters:
E- the type of the pushed elements- Parameters:
historySize- the backlog size, ie. maximum items retained for replay.- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays a limited history to each newSubscriber.
-
create
public static <E> ReplayProcessor<E> create(int historySize, boolean unbounded)
Create a newReplayProcessorthat either replay all the elements or a limited amount of elements depending on theunboundedparameter.- Type Parameters:
E- the type of the pushed elements- Parameters:
historySize- maximum items retained if bounded, or initial link size if unboundedunbounded- true if "unlimited" data store must be supplied- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays the whole history to each newSubscriberif configured as unbounded, a limited history otherwise.
-
createSizeAndTimeout
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> createSizeAndTimeout(int size, Duration maxAge)
Creates a time- and size-bounded replay processor.In this setting, the
ReplayProcessorinternally tags each received item with a timestamp value supplied by theSchedulers.parallel()and holds at mostsizeitems in its internal buffer. It evicts items from the start of the buffer if their age becomes less-than or equal to the supplied age in milliseconds or the buffer reaches itssizelimit.When subscribers subscribe to a terminated
ReplayProcessor, they observe the items that remained in the buffer after the terminal signal, regardless of their age, but at mostsizeitems.If an subscriber subscribes while the
ReplayProcessoris active, it will observe only those items from within the buffer that have age less than the specified time and each subsequent item, even if the buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an subscriber subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for the outdated items at the beginning of the sequence.Note that terminal signals (
onErrorandonComplete) trigger eviction as well. For example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then anonCompletesignal arrives at T=10. If an Subscriber subscribes at T=11, it will find an emptyReplayProcessorwith just anonCompletedsignal.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items observed and emitted by the Processor- Parameters:
maxAge- the maximum age of the contained itemssize- the maximum number of buffered items- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replay up tosizeelements, but will evict them from its history based on their age.
-
createSizeAndTimeout
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> createSizeAndTimeout(int size, Duration maxAge, Scheduler scheduler)
Creates a time- and size-bounded replay processor.In this setting, the
ReplayProcessorinternally tags each received item with a timestamp value supplied by theSchedulerand holds at mostsizeitems in its internal buffer. It evicts items from the start of the buffer if their age becomes less-than or equal to the supplied age in milliseconds or the buffer reaches itssizelimit.When subscribers subscribe to a terminated
ReplayProcessor, they observe the items that remained in the buffer after the terminal signal, regardless of their age, but at mostsizeitems.If an subscriber subscribes while the
ReplayProcessoris active, it will observe only those items from within the buffer that have age less than the specified time and each subsequent item, even if the buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an subscriber subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for the outdated items at the beginning of the sequence.Note that terminal signals (
onErrorandonComplete) trigger eviction as well. For example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then anonCompletesignal arrives at T=10. If an Subscriber subscribes at T=11, it will find an emptyReplayProcessorwith just anonCompletedsignal.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items observed and emitted by the Processor- Parameters:
maxAge- the maximum age of the contained items in millisecondssize- the maximum number of buffered itemsscheduler- theSchedulerthat provides the current time- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replay up tosizeelements, but will evict them from its history based on their age.
-
createTimeout
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> createTimeout(Duration maxAge)
Creates a time-bounded replay processor.In this setting, the
ReplayProcessorinternally tags each observed item with a timestamp value supplied by theSchedulers.parallel()and keeps only those whose age is less than the supplied time value converted to milliseconds. For example, an item arrives at T=0 and the max age is set to 5; at T>=5 this first item is then evicted by any subsequent item or termination signal, leaving the buffer empty.Once the processor is terminated, subscribers subscribing to it will receive items that remained in the buffer after the terminal signal, regardless of their age.
If an subscriber subscribes while the
ReplayProcessoris active, it will observe only those items from within the buffer that have an age less than the specified time, and each item observed thereafter, even if the buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an subscriber subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for any outdated items at the beginning of the sequence.Note that terminal signals (
onErrorandonComplete) trigger eviction as well. For example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then anonCompletesignal arrives at T=10. If an subscriber subscribes at T=11, it will find an emptyReplayProcessorwith just anonCompletedsignal.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items observed and emitted by the Processor- Parameters:
maxAge- the maximum age of the contained items- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays elements based on their age.
-
createTimeout
public static <T> ReplayProcessor<T> createTimeout(Duration maxAge, Scheduler scheduler)
Creates a time-bounded replay processor.In this setting, the
ReplayProcessorinternally tags each observed item with a timestamp value supplied by theSchedulerand keeps only those whose age is less than the supplied time value converted to milliseconds. For example, an item arrives at T=0 and the max age is set to 5; at T>=5 this first item is then evicted by any subsequent item or termination signal, leaving the buffer empty.Once the processor is terminated, subscribers subscribing to it will receive items that remained in the buffer after the terminal signal, regardless of their age.
If an subscriber subscribes while the
ReplayProcessoris active, it will observe only those items from within the buffer that have an age less than the specified time, and each item observed thereafter, even if the buffer evicts items due to the time constraint in the mean time. In other words, once an subscriber subscribes, it observes items without gaps in the sequence except for any outdated items at the beginning of the sequence.Note that terminal signals (
onErrorandonComplete) trigger eviction as well. For example, with a max age of 5, the first item is observed at T=0, then anonCompletesignal arrives at T=10. If an subscriber subscribes at T=11, it will find an emptyReplayProcessorwith just anonCompletedsignal.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items observed and emitted by the Processor- Parameters:
maxAge- the maximum age of the contained items- Returns:
- a new
ReplayProcessorthat replays elements based on their age.
-
currentContext
public Context currentContext()
Description copied from interface:CoreSubscriberRequest aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.- Specified by:
currentContextin interfaceCoreSubscriber<T>- Returns:
- a resolved context or
Context.empty()
-
downstreamCount
public long downstreamCount()
Description copied from class:FluxProcessorReturn the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.- Overrides:
downstreamCountin classFluxProcessor<T,T>- Returns:
- the number of active
Subscriberor -1 if untracked
-
getError
@Nullable public Throwable getError()
Description copied from class:FluxProcessorCurrent error if any, default to null- Overrides:
getErrorin classFluxProcessor<T,T>- Returns:
- Current error if any, default to null
-
getPrefetch
public int getPrefetch()
Description copied from class:FluxThe prefetch configuration of theFlux- Overrides:
getPrefetchin classFlux<T>- Returns:
- the prefetch configuration of the
Flux, -1 if unspecified
-
inners
public Stream<? extends Scannable> inners()
Description copied from interface:ScannableReturn aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)
-
isTerminated
public boolean isTerminated()
Description copied from class:FluxProcessorHas this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?- Overrides:
isTerminatedin classFluxProcessor<T,T>- Returns:
- has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?
-
onComplete
public void onComplete()
- Specified by:
onCompletein interfaceSubscriber<T>
-
onError
public void onError(Throwable t)
- Specified by:
onErrorin interfaceSubscriber<T>
-
onNext
public void onNext(T t)
- Specified by:
onNextin interfaceSubscriber<T>
-
onSubscribe
public void onSubscribe(Subscription s)
Description copied from interface:CoreSubscriberImplementors should initialize any state used bySubscriber.onNext(Object)before callingSubscription.request(long). Should furtheronNextrelated state modification occur, thread-safety will be required.Note that an invalid request
<= 0will not produce an onError and will simply be ignored or reported through a debug-enabledLogger.- Specified by:
onSubscribein interfaceSubscriber<T>- Specified by:
onSubscribein interfaceCoreSubscriber<T>
-
scanUnsafe
@Nullable public Object scanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)
Description copied from interface:ScannableThis method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place. Although it is ignoring the generic type of theScannable.Attrkey, implementors should take care to return values of the correct type, and return null if no specific value is available.For public consumption of attributes, prefer using
Scannable.scan(Attr), which will return a typed value and fall back to the key's default if the component didn't define any mapping.- Specified by:
scanUnsafein interfaceScannable- Overrides:
scanUnsafein classFluxProcessor<T,T>- Parameters:
key- aScannable.Attrto resolve for the component.- Returns:
- the value associated to the key for that specific component, or null if none.
-
subscribe
public void subscribe(CoreSubscriber<? super T> actual)
Description copied from class:FluxAn internalPublisher.subscribe(Subscriber)that will bypassHooks.onLastOperator(Function)pointcut.In addition to behave as expected by
Publisher.subscribe(Subscriber)in a controlled manner, it supports direct subscribe-timeContextpassing.- Specified by:
subscribein classFlux<T>- Parameters:
actual- theSubscriberinterested into the published sequence- See Also:
Flux.subscribe(Subscriber)
-
-