- java.lang.Object
-
- reactor.core.publisher.Flux<OUT>
-
- reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor<IN,OUT>
-
- Type Parameters:
IN- the input value typeOUT- the output value type
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- Processor<IN,OUT>, Publisher<OUT>, Subscriber<IN>, CorePublisher<OUT>, CoreSubscriber<IN>, Disposable, Scannable
- Direct Known Subclasses:
- DirectProcessor, EmitterProcessor, ReplayProcessor, UnicastProcessor
public abstract class FluxProcessor<IN,OUT> extends Flux<OUT> implements Processor<IN,OUT>, CoreSubscriber<IN>, Scannable, Disposable
A base processor that exposesFluxAPI forProcessor. Implementors includeUnicastProcessor,EmitterProcessor,ReplayProcessor.- Author:
- Stephane Maldini
-
-
Nested Class Summary
-
Nested classes/interfaces inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
Scannable.Attr<T>
-
Nested classes/interfaces inherited from interface reactor.core.Disposable
Disposable.Composite, Disposable.Swap
-
-
Field Summary
-
Fields inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
OPERATOR_NAME_UNRELATED_WORDS_PATTERN
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description FluxProcessor()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description ContextcurrentContext()Request aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.voiddispose()Cancel or dispose the underlying task or resource.longdownstreamCount()Return the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.intgetBufferSize()Return the processor buffer capacity if any orInteger.MAX_VALUEThrowablegetError()Current error if any, default to nullbooleanhasCompleted()Return true if terminated with onCompletebooleanhasDownstreams()Return true if anySubscriberis actively subscribedbooleanhasError()Return true if terminated with onErrorStream<? extends Scannable>inners()Return aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)booleanisSerialized()Return true if thisFluxProcessorsupports multithread producingbooleanisTerminated()Has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?ObjectscanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)This method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place.FluxProcessor<IN,OUT>serialize()Create aFluxProcessorthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object).protected booleanserializeAlways()Returns serialization strategy.FluxSink<IN>sink()Create aFluxSinkthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object).FluxSink<IN>sink(FluxSink.OverflowStrategy strategy)Create aFluxSinkthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object).static <T> FluxProcessor<Publisher<? extends T>,T>switchOnNext()Build aFluxProcessorwhose data are emitted by the most recent emittedPublisher.static <IN,OUT> FluxProcessor<IN,OUT>wrap(Subscriber<IN> upstream, Publisher<OUT> downstream)-
Methods inherited from class reactor.core.publisher.Flux
all, any, as, blockFirst, blockFirst, blockLast, blockLast, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferUntil, bufferUntil, bufferUntilChanged, bufferUntilChanged, bufferUntilChanged, bufferWhen, bufferWhen, bufferWhile, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cancelOn, cast, checkpoint, checkpoint, checkpoint, collect, collect, collectList, collectMap, collectMap, collectMap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectSortedList, collectSortedList, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, concat, concat, concat, concat, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatMap, concatMap, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapIterable, concatMapIterable, concatWith, concatWithValues, count, create, create, defaultIfEmpty, defer, deferWithContext, delayElements, delayElements, delaySequence, delaySequence, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delayUntil, dematerialize, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, doAfterTerminate, doFinally, doFirst, doOnCancel, doOnComplete, doOnDiscard, doOnEach, doOnError, doOnError, doOnError, doOnNext, doOnRequest, doOnSubscribe, doOnTerminate, elapsed, elapsed, elementAt, elementAt, empty, error, error, error, expand, expand, expandDeep, expandDeep, filter, filterWhen, filterWhen, first, first, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMapDelayError, flatMapIterable, flatMapIterable, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequentialDelayError, from, fromArray, fromIterable, fromStream, fromStream, generate, generate, generate, getPrefetch, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupJoin, handle, hasElement, hasElements, hide, ignoreElements, index, index, interval, interval, interval, interval, join, just, just, last, last, limitRate, limitRate, limitRequest, log, log, log, log, log, log, map, materialize, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, mergeDelayError, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrderedWith, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeWith, metrics, name, never, next, ofType, onAssembly, onAssembly, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureError, onBackpressureLatest, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorStop, onTerminateDetach, or, parallel, parallel, parallel, publish, publish, publish, publish, publishNext, publishOn, publishOn, publishOn, push, push, range, reduce, reduce, reduceWith, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeatWhen, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, retry, retry, retryWhen, sample, sample, sampleFirst, sampleFirst, sampleTimeout, sampleTimeout, scan, scan, scanWith, share, single, single, singleOrEmpty, skip, skip, skip, skipLast, skipUntil, skipUntilOther, skipWhile, sort, sort, startWith, startWith, startWith, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribeOn, subscribeOn, subscriberContext, subscriberContext, subscribeWith, switchIfEmpty, switchMap, switchMap, switchOnFirst, switchOnFirst, switchOnNext, switchOnNext, tag, take, take, take, takeLast, takeUntil, takeUntilOther, takeWhile, then, then, thenEmpty, thenMany, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timestamp, timestamp, toIterable, toIterable, toIterable, toStream, toStream, toString, transform, transformDeferred, using, using, usingWhen, usingWhen, window, window, window, window, window, window, window, windowTimeout, windowTimeout, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowUntilChanged, windowUntilChanged, windowUntilChanged, windowWhen, windowWhile, windowWhile, withLatestFrom, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWithIterable, zipWithIterable
-
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait
-
Methods inherited from interface reactor.core.CoreSubscriber
onSubscribe
-
Methods inherited from interface org.reactivestreams.Subscriber
onComplete, onError, onNext
-
Methods inherited from interface reactor.core.Scannable
actuals, from, isScanAvailable, name, parents, scan, scanOrDefault, stepName, steps, tags
-
Methods inherited from interface reactor.core.Disposable
isDisposed
-
-
-
-
Method Detail
-
currentContext
public Context currentContext()
Description copied from interface:CoreSubscriberRequest aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.- Specified by:
currentContextin interfaceCoreSubscriber<IN>- Returns:
- a resolved context or
Context.empty()
-
dispose
public void dispose()
Description copied from interface:DisposableCancel or dispose the underlying task or resource.Implementations are required to make this method idempotent.
- Specified by:
disposein interfaceDisposable
-
downstreamCount
public long downstreamCount()
Return the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.- Returns:
- the number of active
Subscriberor -1 if untracked
-
getBufferSize
public int getBufferSize()
Return the processor buffer capacity if any orInteger.MAX_VALUE- Returns:
- processor buffer capacity if any or
Integer.MAX_VALUE
-
getError
@Nullable public Throwable getError()
Current error if any, default to null- Returns:
- Current error if any, default to null
-
hasCompleted
public final boolean hasCompleted()
Return true if terminated with onComplete- Returns:
- true if terminated with onComplete
-
hasDownstreams
public boolean hasDownstreams()
Return true if anySubscriberis actively subscribed- Returns:
- true if any
Subscriberis actively subscribed
-
hasError
public final boolean hasError()
Return true if terminated with onError- Returns:
- true if terminated with onError
-
inners
public Stream<? extends Scannable> inners()
Description copied from interface:ScannableReturn aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)
-
isSerialized
public boolean isSerialized()
Return true if thisFluxProcessorsupports multithread producing- Returns:
- true if this
FluxProcessorsupports multithread producing
-
isTerminated
public boolean isTerminated()
Has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?- Returns:
- has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?
-
scanUnsafe
@Nullable public Object scanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)
Description copied from interface:ScannableThis method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place. Although it is ignoring the generic type of theScannable.Attrkey, implementors should take care to return values of the correct type, and return null if no specific value is available.For public consumption of attributes, prefer using
Scannable.scan(Attr), which will return a typed value and fall back to the key's default if the component didn't define any mapping.- Specified by:
scanUnsafein interfaceScannable- Parameters:
key- aScannable.Attrto resolve for the component.- Returns:
- the value associated to the key for that specific component, or null if none.
-
serialize
public final FluxProcessor<IN,OUT> serialize()
Create aFluxProcessorthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object).- Returns:
- a serializing
FluxProcessor - onDiscard Support
- The resulting processor discards elements received from the source
Publisher(if any) when it cancels subscription to said source.
-
serializeAlways
protected boolean serializeAlways()
Returns serialization strategy. If true,sink()will always be serialized. Otherwise sink is serialized only ifFluxSink.onRequest(java.util.function.LongConsumer)is invoked.- Returns:
- true to serialize any sink, false to delay serialization till onRequest
-
sink
public final FluxSink<IN> sink()
Create aFluxSinkthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object). This processor will be subscribed to thatFluxSink, and any previous subscribers will be unsubscribed.The returned
FluxSinkwill not apply anyFluxSink.OverflowStrategyand overflowingFluxSink.next(Object)will behave in two possible ways depending on the Processor:- an unbounded processor will handle the overflow itself by dropping or buffering
- a bounded processor will block/spin
- Returns:
- a serializing
FluxSink
-
sink
public final FluxSink<IN> sink(FluxSink.OverflowStrategy strategy)
Create aFluxSinkthat safely gates multi-threaded producerSubscriber.onNext(Object). This processor will be subscribed to thatFluxSink, and any previous subscribers will be unsubscribed.The returned
FluxSinkwill not apply anyFluxSink.OverflowStrategyand overflowingFluxSink.next(Object)will behave in two possible ways depending on the Processor:- an unbounded processor will handle the overflow itself by dropping or buffering
- a bounded processor will block/spin on IGNORE strategy, or apply the strategy behavior
- Parameters:
strategy- the overflow strategy, seeFluxSink.OverflowStrategyfor the available strategies- Returns:
- a serializing
FluxSink
-
switchOnNext
public static <T> FluxProcessor<Publisher<? extends T>,T> switchOnNext()
Build aFluxProcessorwhose data are emitted by the most recent emittedPublisher. TheFluxwill complete once both the publishers source and the last switched toPublisherhave completed.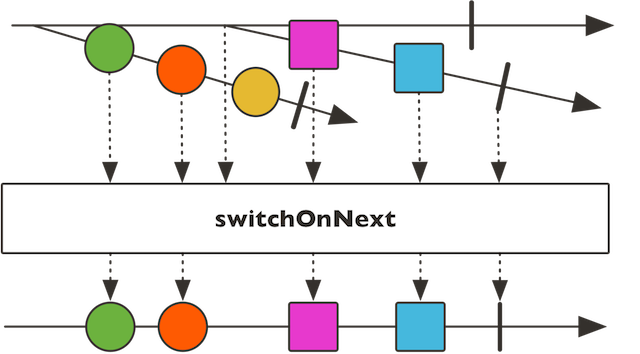
- Type Parameters:
T- the produced type- Returns:
- a
FluxProcessoraccepting publishers and producing T
-
wrap
public static <IN,OUT> FluxProcessor<IN,OUT> wrap(Subscriber<IN> upstream, Publisher<OUT> downstream)
Transform a receivingSubscriberand a producingPublisherin a logicalFluxProcessor. The link between the passed upstream and returned downstream will not be created automatically, e.g. not subscribed together. AProcessormight choose to have orthogonal sequence input and output.- Type Parameters:
IN- the receiving typeOUT- the producing type- Parameters:
upstream- the upstream subscriberdownstream- the downstream publisher- Returns:
- a new blackboxed
FluxProcessor
-
-